ISRO always gives us the opportunity to feel proud from time to time. After the successful landing of Chandrayaan-3 on the south pole of the Moon, it is now time for a mission related to the most important thing in our solar system, the Sun, which is the reason for life on Earth. Let’s take a look at some important aspects related to this crucial mission by ISRO.
ISRO’s Aditya-L1 Mission
- Aditya was first conceptualized by the Advisory Committee for Space Research in the year 2008. The initial focus of this mission was quite modest, primarily aimed at smaller objectives. However, in the years 2016-2017, the mission was expanded to create a comprehensive solar and space environment observatory to be placed at Lagrange point L1. Therefore, the name of this mission was changed to Aditya-L1.
- ISRO launched the Aditya-L1 mission on September 2, 2023, and with this mission, ISRO has joined the ranks of three space agencies that have launched orbiter-based missions to the Sun. Prior to this, only NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA) had undertaken such missions.
- The budget for ISRO’s Aditya-L1 mission is approximately ₹400 crore, which is equivalent to $48 million.
- The project director of this mission is Nigar Shaji.

- ISRO successfully launched the Aditya-L1 mission from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh, on September 2, 2023, using the PSLV-C57 rocket.
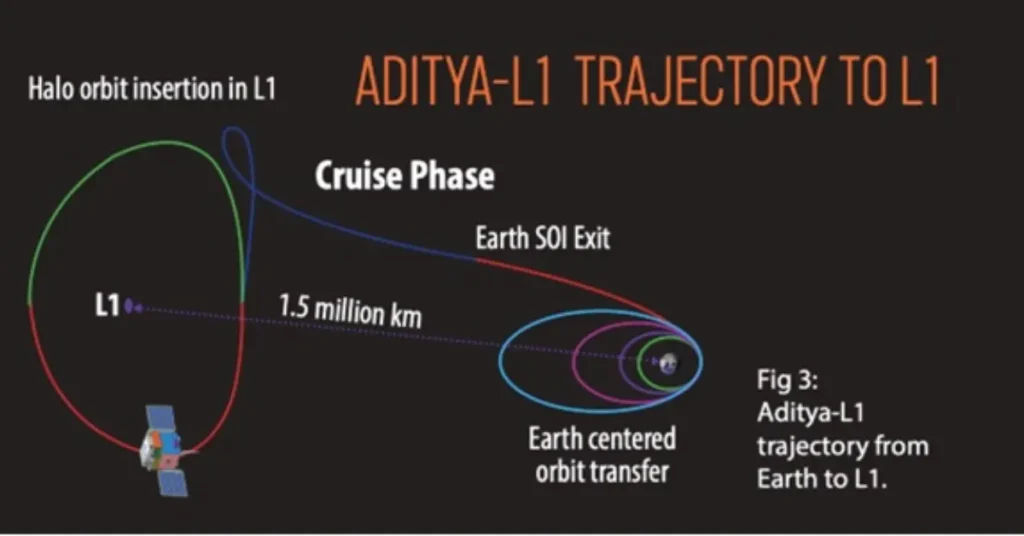
- It will take Aditya-L1 approximately 4 months to reach its desired point, covering a distance of about 1.5 million km. This distance represents approximately 1% of the distance between the Sun and Earth, which is approximately 150.95 million km.
- The Aditya-L1 mission is expected to have a duration of approximately 5 years. Over these 5 years, it will gather significant information about the Sun, which will be discussed further.
What is L1? (Lagrange 1)
The “L1” in the name of this mission is quite significant. During the Aditya-L1 mission, it will be placed at a point called ‘Lagrange point 1,’ which is located about 1.5 million kilometers away from Earth. This is why the mission is named with an “L1.”
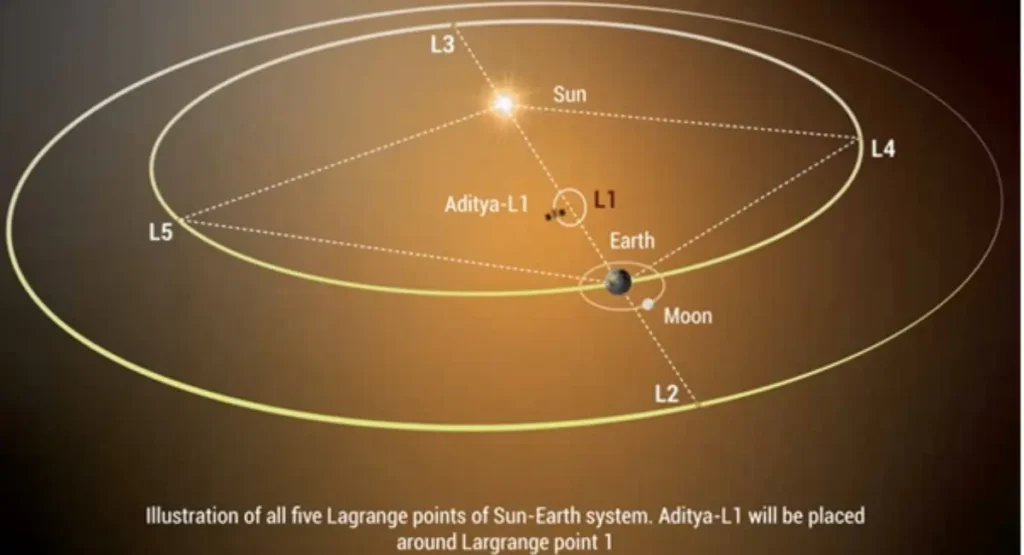
The concept of Lagrange points was introduced by an Italian-French mathematician named Joseph-Louis Lagrange. He proposed – when two large objects are in space, there is a gravitational point between them where something can be placed with minimal gravitational interference.
ISRO’s Aditya-L1 payloads and mission objectives
Aditya-L1’s mission objectives
Understanding the Sun, which is the reason for life on our Earth, and how it reacts, as well as the effects it has on our Earth, is crucial for us. Through this mission, we can learn a lot about the Sun. For example –
Coronal Heating Mechanism.
Solar Wind and Magnetic Field Studies.
Space Weather Prediction.
Understanding Earth’s Climate.
Origin and Dynamics of CMEs (coronal mass ejections).
Comprehensive Solar Atmosphere Imaging.
Also Read – First Images of Moon clicked by Chandrayaan-3
Aditya-L1’s Payloads
Aditya-L1 has 7 such things that will help it analyze the Sun effectively.
Remote Sensing Payloads
- 1. Visible Emission Line Coronagraph
(VELC) – Corona/Imaging & Spectroscopy. - 2. High Energy L1 Orbiting X-ray Spectrometer(HEL1OS) – Hard X-ray spectrometer: Sun-as-a-star observation.
- 3. Solar Low Energy X-ray Spectrometer (SoLEXS) – Soft X-ray spectrometer: Sun-as-a-star observation.
- 4. Solar Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (SUIT) – Photosphere and Chromosphere Imaging- Narrow & Broadband.
- Original Position Payloads
Original Position Payloads
- 5. Aditya Solar wind Particle Experiment(ASPEX) – Solar wind/Particle Analyzer Protons & Heavier Ions with directions.
- 6. Plasma Analyser Package For Aditya (PAPA) – Solar wind/Particle Analyzer Electrons & Heavier Ions with directions.
- 7. Advanced Tri-axial High Resolution Digital Magnetometers – In-situ magnetic field (Bx, By and Bz).
Must Read – Chandrayaan-3: Everything about ISRO’s Successful Moon Mission
Objective of payloads
The objectives of these 7 regions are also quite diverse. It will analyze the significant events that directly impact our Earth. Such as –
- Solar Winds.
- UV Solar Radiation.
- Solar Magnetic Storms.
“All these things directly influence our Earth.”
If you liked this article, be sure to share it with your friends so that they can also learn about this amazing news.
